Malaria parasites are sporozoans and belongs to order Haemosporida. The genus Plasmodium has been subdivided into nine subgenera, of which three are found in mammals, four in birds and two in lizards. According to the classification, Plasmodium vivax, Plasmodium ovale and Plasmodium malariae belong to the subgenus Plasmodium, and Plasmodium falciparum belongs to the subgenera Laverania.
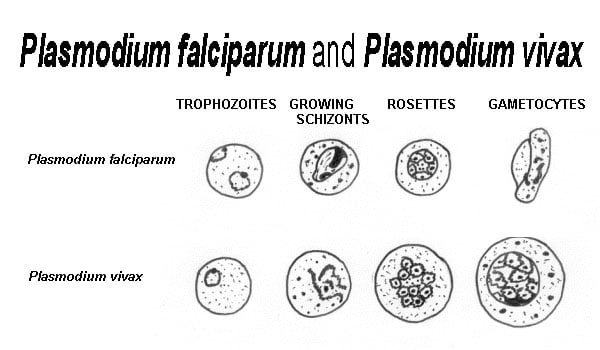
Differences Between Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax with characters are given below:
| Characteristics | P. faciparum | P. vivax |
|---|---|---|
Duration of asexual phase in man | 36-48 hrs Usually 48 hrs | 48 hrs |
Duration of sporogony in mosquito | 22-23 days at 20°C 10-12 days at 27°C | 30 days at 17.5°C 10 days at 25-30°C |
Duration of intrahepatic phase | 5.5 days | 8 days |
Duration of Schizogony | 12 days | 14 days |
Forms found in the smear | Rings and banana shaped gametocytes | Trophozoites, schizonts and gametocytes |
Level of usual maximum parasitemia | May exceed 200,000/µl, commonly 50,000/µl | Up to 30,000/µl of blood |
No. of merozoites released per infected hepatocyte | 30,000 | 10,000 |
Red cell preference | Younger cells (but can invade cells of all ages) | Reticulocytes and red cells up to 2 weeks old |
Parasitized Red cells | Not enlarge. Coarse stippling (Maurer’s clefts) | Enlarged, pale. Fine stippling (Schuffner’s dots) |
Pigment Color | Black and Dark Brown | Yellow or Golden Brown |
Ability to cause relapses | No | Yes |
Ring Stage Trophozoite | Small rings (1/5 red cell diameter). Often two granules. Multiple rings common. | Large rings (1/3 to 1/2 diameter). Single chromatin granule. Two rings in one cell. |
Pigment in developing trophozoites | Coarse, black, few clumps | Fine, Light brown, scattered |
Late Trophozoite | Compact Medium Sized Rarely amoeboid Vacuole inconspicuous. | Pleomorphic Large Markedly amoeboid Vacuole prominent. |
Schizont | Small, compact, Single pigmented mass Seldom seen in the peripheral blood smear | Large, amoeboid, Pigments coarse Can be seen in the blood smear |
Mature Schizont (segmenters) | 8-16 (Usually 8-18). | 12-14 (Usually 12-18) |
Microgametocytes | Kidney-shaped with blunt round ends. Cytoplasm stains pale blue. Nucleus large. Chromatin diffuse. Granules fine, scattered. | Spherical, compact. Cytoplasm stains pale light blue. Chromatin undivided. Granules abundant. |
Macrogametocytes | Crescentic. Cytoplasm stains dark blue. Nucleus compact. Chromatin central. Pigment more compact. | Spherical. Cytoplasm stains dark blue. Nucleus small. Pigment diffuse ecoarse. |
Disease | Malignant tertian malaria | Benign tertian malaria |

Monoclonal antibody therapy is a form of immunotherapy that uses monoclonal antibodies (mAb) to bind monospecifically to certain cells or proteins. This may then stimulate the patient’s immune system to attack those cells.
Monoclonal antibody therapy is a form of immunotherapy that uses monoclonal antibodies (mAb) to bind monospecifically to certain cells or proteins. This may then stimulate the patient’s immune system to attack those cells…
Sanjay Kataria MSc (Med Microbiology) NIMS
in my openion .it will be batter if you add clinical difference in between and importance of immidiate measures eg. treatment etc.
Dr.K.C.Chaudhary MBBS, MD (Path. & Bact.) .Rtd. JD medical and health serviceses Govt. of UP.