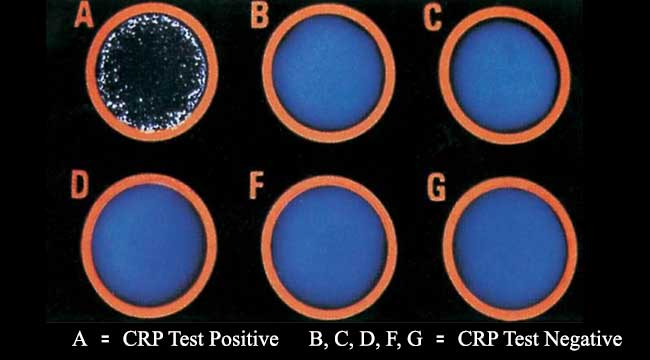
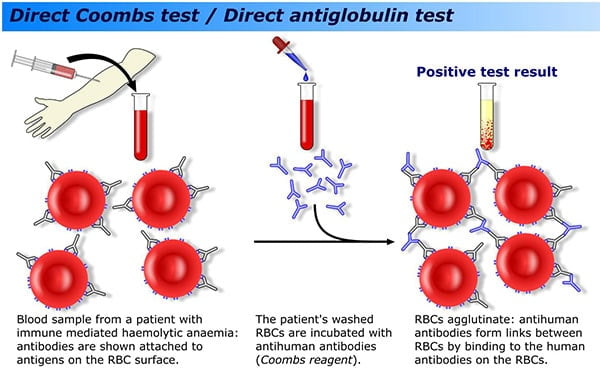
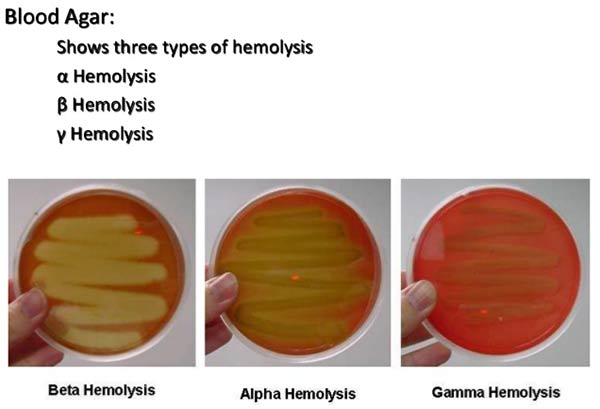
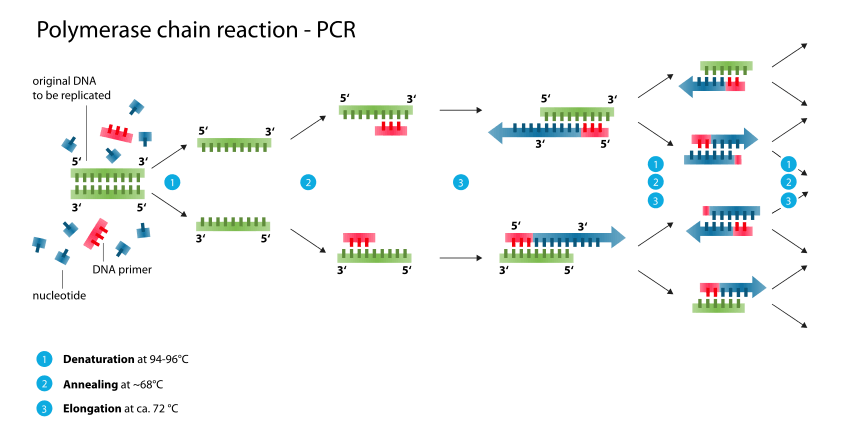
Good Laboratory Practices
Good Laboratory Practices (GLP) is an official regulation that was created by the FDA in 1978. Good Laboratory Practice (GLP) is a quality system concerned with the organizational process and the conditions under which non-clinical health and environmental safety studies are planned, performed, monitored, recorded, … Read more