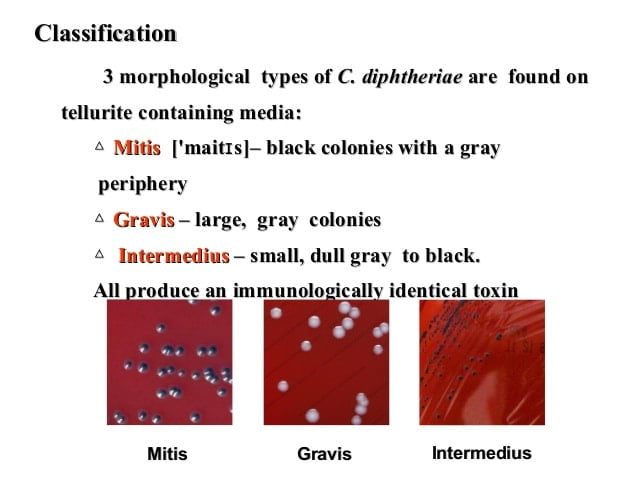
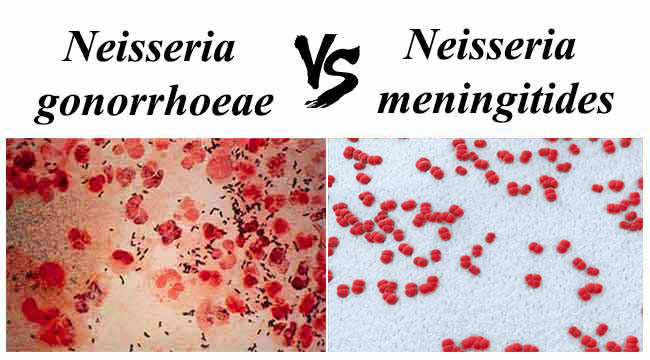
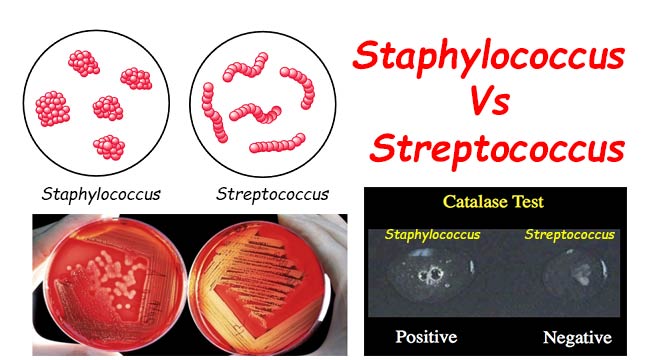
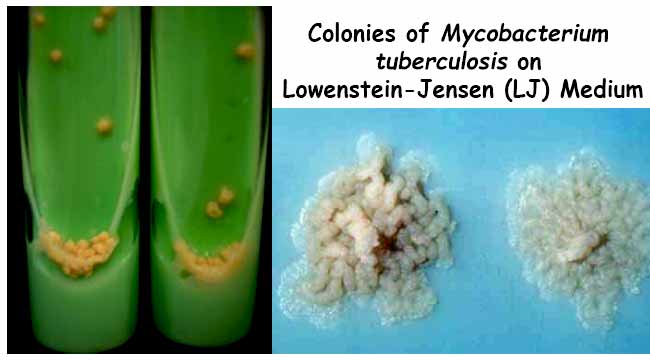
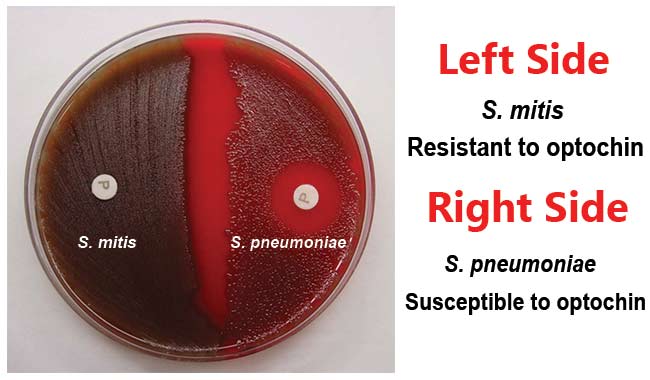
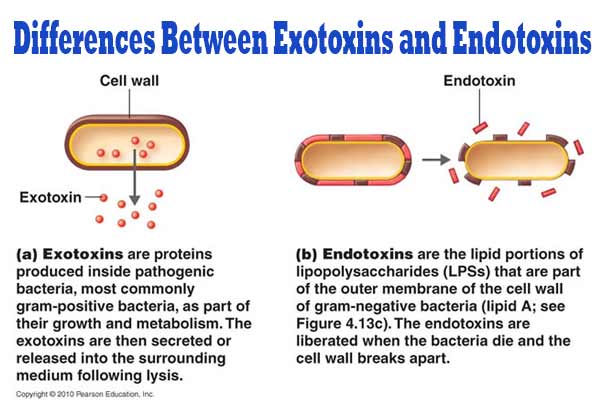
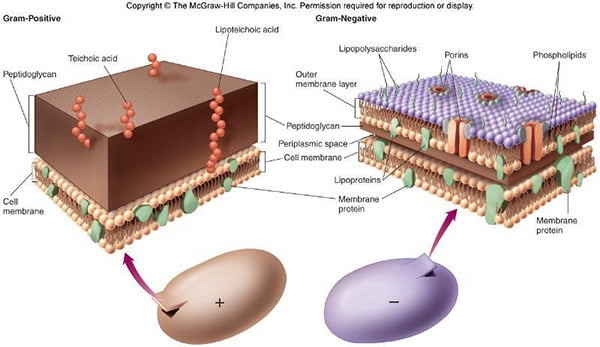
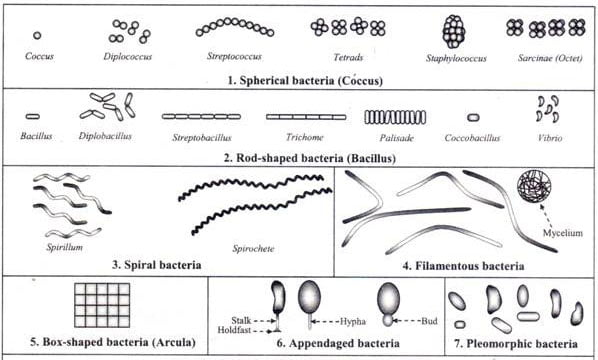
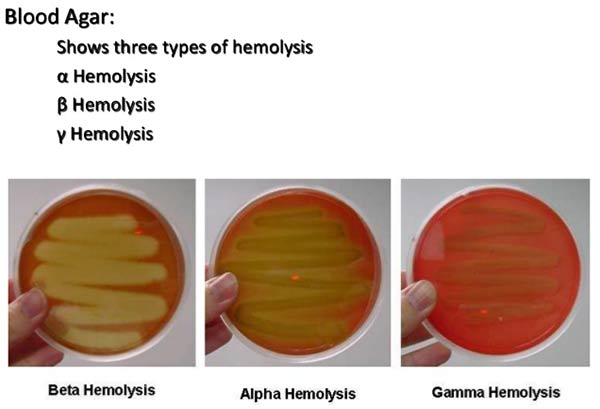
Biotypes of Corynebacterium Diphtheriae
Corynebacterium diphtheriae is a nonmotile, noncapsulated, club-shaped, gram-positive bacillus. Toxigenic strains are lysogenic for one of a family of corynebacteriophages that carry the structural gene for diphtheria toxin, tox. Corynebacterium diphtheriae is classified into biotypes (mitis, intermedius, and gravis) according to colony morphology, as well … Read more