| Basic Characteristics | Properties (Proteus mirabilis) |
|---|---|
| Capsule | Negative (-ve) |
| Catalase | Positive (+ve) |
| Citrate | Positive (+ve) |
| Flagella | Positive (+ve) |
| Gas from Glucose | Positive (+ve) |
| Gelatin Hydrolysis | Positive (+ve) |
| Gram Staining | Negative (-ve) |
| Growth in KCN | Positive (+ve) |
| H2S | Positive (+ve) |
| Indole | Negative (-ve) |
| Motility | Positive (+ve) |
| MR (Methyl Red) | Positive (+ve) |
| Nitrate Reduction | Positive (+ve) |
| OF (Oxidative-Fermentative) | Facultative anaerobes |
| Oxidase | Negative (-ve) |
| Pigment | Negative (-ve) |
| Shape | Rods |
| Spore | Negative (-ve) |
| Urease | Positive (+ve) |
| VP (Voges Proskauer) | Negative (-ve) |
| Fermentation of | |
| Adonitol | Negative (-ve) |
| Arabinose | Negative (-ve) |
| Arabitol | Negative (-ve) |
| Cellobiose | Negative (-ve) |
| DNase | Variable |
| Dulcitol | Negative (-ve) |
| Erythritol | Negative (-ve) |
| Glucose | Positive (+ve) |
| Glycerol | Positive (+ve) |
| Inositol | Negative (-ve) |
| Lactose | Negative (-ve) |
| Malonate | Negative (-ve) |
| Maltose | Negative (-ve) |
| Mannitol | Negative (-ve) |
| Mannose | Negative (-ve) |
| Melibiose | Negative (-ve) |
| Mucate | Negative (-ve) |
| MyoInositol | Negative (-ve) |
| Raffinose | Negative (-ve) |
| Rhamnose | Negative (-ve) |
| Salicin | Negative (-ve) |
| Sorbitol | Negative (-ve) |
| Starch | Negative (-ve) |
| Sucrose | Negative (-ve) |
| Tartrate | Positive (+ve) |
| Trehalose | Positive (+ve) |
| Xylose | Positive (+ve) |
| Enzymatic Reactions | |
| Acetate Utilization | Negative (-ve) |
| Aesculine Hydrolysis | Negative (-ve) |
| Casein Hydrolysis | Negative (-ve) |
| Esculin Hydrolysis | Negative (-ve) |
| Lipase | Positive (+ve) |
| Lysine decarboxylases | Negative (-ve) |
| ONPG (β-galactosidase) | Negative (-ve) |
| Ornithine Decarboxylase | Positive (+ve) |
| Pectate Degradation | Negative (-ve) |
| Phenylalanine Deaminase | Positive (+ve) |
| Tryptophan Deaminase | Negative (-ve) |

What are the biochemical test and identification of Proteus vulgaris?
first and foremost the most identifications of test for proteus spp by urease test ,PPA
The socond biochemical test indole the are defrenciate to p. Mirabilis from p vulgaris. If indole positve_ P.vllulgaris if negative – P.mirabilis
P.vulgaris is urease + within 3 hours, PPA +, methyl red +, cirrate +, lactose -, maltose +, sucrose +, ornithine decarboxylase -, Gram -,ve rod and actively motile.
Indole +
MR +
VP-
CITRATE –
GAS –
H2S +
LYSINE –
UREASE +
PHENYLALINE +
MOTILITY +
may I know the result for coagulase test?
What is best identification of corynebacterium diphtheria
Loefler’s serum slant or Tindales agar are selective media for cornye. Cornye has a particular look on the Tinsdale agar. Then you’ll do your regular gram stains (Gram Positive bacilli, sometimes with club shape), catalase (positive), urease test (negative), growth is not supported on a MacConkey agar. Albert stain for confirmation to show green tail and reddish metachromatic granules. Carbohydrate Fermentation test: Maltose- Negative , Dextrose-Positive, Starch-Positive, Sucrose-Negative. The positive results for the starch and the negative results for the sucrose show the presence of a species of Corynebacterium diphtheriae (gravis).
what is media choice of growing Proteus mirabilis
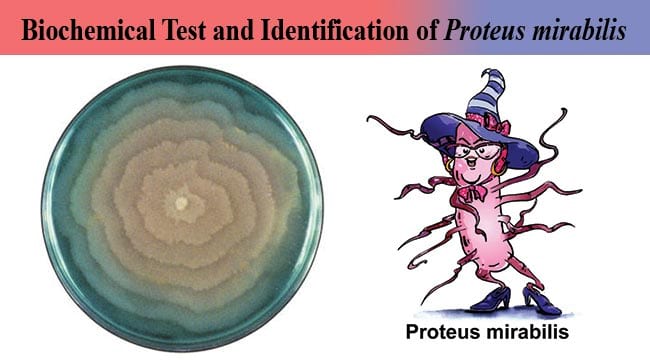
Nutrient agar is always a safe choice. MacConkey is usually fairly decent, especially if you want to test the lactose fermentation thing. Finally, blood agar is always really cool for p. mirabilis, because the organism has a tendency to swarm across the agar (because of it’s high motility), so that’s cool to see.