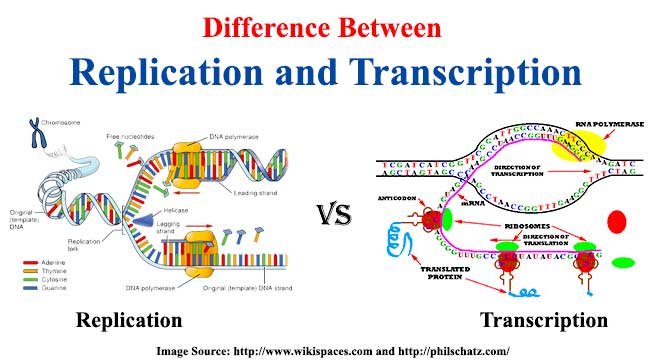
| 1. | Definition | DNA replication is the process of making two daughter strand where each daughter strand contains half of the original DNA double helix. | Transcription is the process of synthesis of RNA using DNA as a template. |
| 2. | Purpose | To conserve the entire genome for next generation. | To make RNA copies of individual genes. |
| 3. | Enzymes Required | DNA Helicase, DNA Polymerase | Transcriptase (type of DNA Helicase), RNA polymerase |
| 4. | Occurrence | Occurs in the S phase of cell cycle. | Occurs in the G1 and G2 phases of cell cycle. |
| 5. | Raw Materials | dATP, dGTP, dTTP and dCTP serve as raw materials. | ATP, UTP, GTP and CTP serve as raw materials. |
| 6. | Occurrence | Occurs along the strands of DNA. | Occurs along one strand of DNA. |
| 7. | Occurrence | Occurs in preparation for cell division. | Occurs in preparation for protein translation. |
| 8. | Bond | Replicated DNA strand remains hydrogen bonded to its template DNA strand. | Transcribed RNA strand separates from its DNA template strand. |
| 9. | Primers | It require RNA primer to start replication. | No primer is required to start. |
| 10. | Products | Two Daughter Strands | mRNA, tRNA, rRNA and non-coding RNA( like microRNA) |
| 11. | Products | Products remain within nucleus. | Greater part of the product passes from nucleus into the cytoplasm. |
| 12. | Products | Products are not degraded. | Products are degraded after their function of over. |
| 13. | Copying | It involves copying of the entire genome. | It involves copying of certain individual genes only. |
| 14. | Unwinding and Splitting | It involves unwinding and splitting of the entire DNA molecule. | It involves unwinding and splitting of only those genes which are to be transcribed. |
| 15. | Processing | It produces normal DNA molecules that do not need any processing. | It produces primary RNA transcript molecule which needs processing to acquire final form and size. |