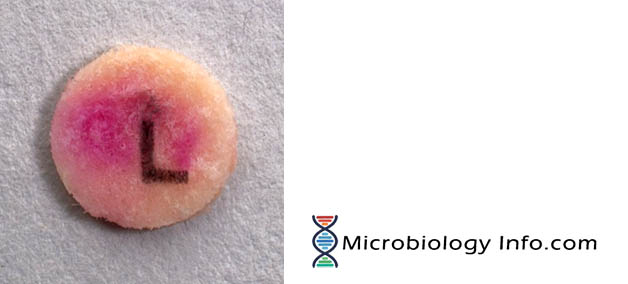
Leucine amino peptidase (LAP) test is a rapid test for detection of enzyme leucine aminopeptidase. Leucine- β- napthalamide impregnated disk serves as a substrate for the detection of leucine aminopeptidase. This test is usually used, in conjunction with other tests, for the identification of streptococci and other catalase negative gram positive cocci.
Objective
To perform the preliminary characterization of catalase negative, gram-positive cocci.
Principle
The LAP disk is a rapid test for the detection of enzyme leucine amino peptidase. The disks are impregnated with leucine-ß-naphthylamide, which is hydrolyzed by the enzyme leucine aminopeptidase, produced by LAP positive organisms. This enzymatic activity results in the release of ß-naphthylamine, which couples with p-dimethylaminocinnamaldehyde reagent, when it is added, to form a highly visible red Schiff base.
Method
- Aseptically place a LAP disk in a sterile petri dish, and allow disk to warm to room temperature
- Slightly dampen the LAP disk with reagent grade water or with a small amount of sterile distilled water.
- Using a wooden applicator stick, rub a small amount of several colonies of an 18 to 24 hour pure culture onto a small area of the LAP disk.
- Incubate at room temperature for 5 minutes.
- After the incubation period, add 1 drop of cinnamaldehyde reagent and read within one minute.
Expected results
- Positive: Development of a red/pink color
- Negative: No change or a slight yellow color
Uses
- The LAP test is often used in conjunction with PYR and other biochemical tests to help differentiate between catalase, gram-positive cocci.
- In general, Streptococcus pneumoniae and Streptococcus pyogenes, Pediococcus, Lactococcus, and Enterococcus species are all LAP positive, while other beta-hemolytic Streptococci, Aerococcus and Leuconostoc species are LAP negative which help in their identification.
- Aminopeptidase Test has been used to perform a Gram analysis of bacteria isolated from Scleroderma citrinum mycorrhizae, the mycorrhizosphere and bulk soil.
Limitations
- The test organism should be confirmed to be gram- positive coccus and catalase negative before performing the LAP test.
- Adequate inoculums should be ensured otherwise false negatives may occur
- Streptococci should be tested prior to 48-hour incubation or subcultured prior to testing.
References
- www.dalynn.com/dyn/ck_assets/files/tech/DL10.pdf
- https://assets.thermofisher.com/TFS-Assets/LSG/manuals/IFU21129.pdf
- https://eportal.mountsinai.ca/Microbiology/manual/tech/tech23.pdf
- https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/product/sial/75554?lang=en®ion=NP
Similar Posts:
- PYR Test- Principle, Uses, Procedure and Result Interpretation
- Catalase Test- Principle, Uses, Procedure, Result Interpretation with Precautions
- Indole Test- Principle, Reagents, Procedure, Result Interpretation and Limitations
- Oxidase Test- Principle, Uses, Procedure, Types, Result Interpretation, Examples and Limitations