Salmonella Shigella (SS) Agar is moderately selective and differential medium for the isolation, cultivation and differentiation of Salmonella spp. and some strains of Shigella spp. SS Agar is a modification of the Desoxycholate Citrate Agar. It is recommended for testing clinical specimens and food testing for the presence of Salmonella spp. and some Shigella spp.
Composition of Salmonella Shigella Agar
| Ingredients | Gms / Litre |
|---|---|
| Beef Extract | 5.00 |
| Enzymatic Digest of Casein | 2.50 |
| Enzymatic Digest of Animal Tissue | 2.50 |
| Lactose | 10.00 |
| Bile Salts | 8.50 |
| Sodium Citrate | 8.50 |
| Sodium Thiosulfate | 8.50 |
| Ferric Citrate | 1.00 |
| Brilliant Green | 0.00033 |
| Neutral Red | 0.025 |
| Agar | 13.50 |
Distilled Water = 1000 ml
pH ( at 25°C) 7.0 ± 0.2
Principle of Salmonella Shigella Agar
The inclusion of Bile Salts, Sodium Citrate and Brilliant Green serve to inhibit gram-positive, coliform organisms and inhibit swarming Proteus spp., while allowing Salmonella spp. to grow. Beef Extract, Enzymatic Digest of Casein, and Enzymatic Digest of Animal Tissue provide sources of nitrogen, carbon, and vitamins required for organism growth. Lactose is the carbohydrate present in Salmonella Shigella Agar. Thiosulfate and Ferric Citrate permit detection of hydrogen sulfide by the production of colonies with black centers. Neutral red turns red in the presence of an acidic pH, thus showing fermentation has occurred.
Uses of Salmonella Shigella Agar
- It is used as a selective and differential medium for the isolation of Salmonella and some Shigella species from clinical and non-clinical specimens.
- This medium is not recommended for the primary isolation of Shigella.
- It was also developed to aid in the differentiation of lactose and non-lactose-fermenters from clinical specimens, suspected foods, and other such samples.
Preparation of Salmonella Shigella Agar
- Suspend 60.0 grams of Salmonella Shigella Agar in 1000 ml distilled water.
- Heat to boiling to dissolve the medium completely.
- Do not autoclave.
- Mix well and pour into sterile Petri plates.
Result Interpretation on Salmonella Shigella Agar
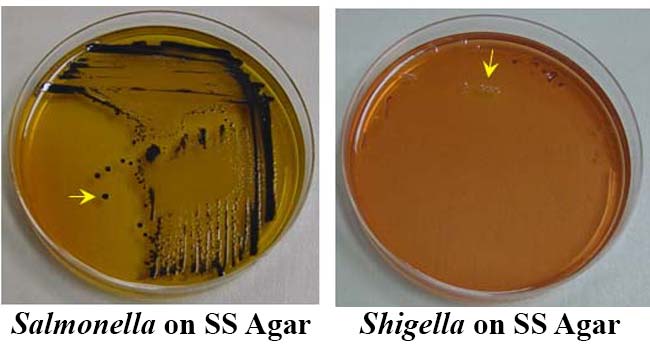
Salmonella will not ferment lactose, but produce hydrogen sulfide (H2S) gas. The resulting bacterial colonies will appear colorless with black centers.
Shigella do not ferment lactose or produce hydrogen sulfide gas, so the resulting colonies will be colorless.
Coliform bacteria such as E. coli will ferment the lactose in the media, resulting in bacterial growth with a pink color. They do not produce any hydrogen sulfide.
Enterobacter and Klebsiella appears larger than E. coli, mucoid, pale, opaque cream to pink.
Quality Control on Salmonella Shigella Agar
Positive
Salmonella enteriditis ATCC 13076= Colorless colonies with black center
Salmonella typhi ATCC 6539 = Colorless colonies with black center
Salmonella typhimurium ATCC 14028= Colorless colonies with black center
Shigella flexneri ATCC 12022 = Colorless colonies
Negative
Enterococcus faecalis ATCC 19433 = Inhibited
Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 = Inhibited
Enterobacter aerogenes ATCC 13048 = partially inhibited. Cream-pink
Limitations of Salmonella Shigella Agar
- It is recommended that biochemical, immunological, molecular, or mass spectrometry testing be performed on colonies from pure culture for complete identification.
- The incorporation of brilliant green into this medium makes it highly selective, and has been shown to inhibit the growth of some Shigella
- The bile salts may crystallize over time. They appear as small spider-like puff balls within the medium and do not affect the performance of the medium.
- Some strains of Shigella, such as sonneiand S. dysenteriae serovar 1, may ferment lactose relatively slowly, and colonies change to lactose-fermenting after cultivation for 2 or more days.
- A few non-pathogenic organisms may grow on Salmonella Shigella
References
- SS Agar. Hardy Diagnostics.
- Salmonella-Shigella Collin County Community College District.
- Salmonella Shigella Agar (SS Agar). Oxoid Limited. Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
- SS Agar – Salmonella Shigella Agar (Medium). Microbiology Made Easy.
- Salmonella-Shigella Agar Culture Media. My Bio Source.
- SS agar. BioMerieux.
- Salmonella Shigella Remel.
- Salmonella Shigella Agar. Becton, Dickinson and Company.
- Salmonella Shigella Agar (7152). Acumedia Manufacturers, Inc.
- Salmonella Shigella Agar (SS Agar). Laboratorios Conda, S.A.
- SS Agar (Salmonella Shigella Agar) Plate. HiMedia Laboratories Pvt. Ltd.
- 85640 SS-Agar (Salmonella Shigella Agar). Sigma-Aldrich, Inc.
Similar Posts:
- Simmons Citrate Agar- Composition, Principle, Uses, Preparation and Result Interpretation
- Xylose Lysine Deoxycholate (XLD) Agar- Principle, Uses, Composition, Preparation and Colony Characteristics
- List of culture media used in microbiology with their uses
- Kligler’s Iron Agar Test – Procedure, Uses and Interpretation

thank you very much, i would like to know much about. 1: Incubation period, 2: how long will it take for the result to come out. 3: prepared SSA will stay for how long?.
I would also like to know. I used to use XLD for Salmonella analyses for pharmacy industry, the incubation was 24 – 36 hours, and could last for 4 weeks (i have validated it) and now will change to SSA. is it the same?
Thank you very much. This was helpful. Are there any species of Salmonella that grow as white colonies on SS media