Although mature lymphocytes all look pretty much alike, they are extraordinarily diverse in their functions. The most abundant lymphocytes are:
B lymphocytes (often simply called B cells) and
T lymphocytes (likewise called T cells).
Some of the differences between B Cells and T Cells are as follows:
| S.N. | Properties | B-Cells | T-Cells |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Name | B lymphocytes | T lymphocytes |
| 2 | Origin | Bone Marrow | Thymus |
| 3 | Position | Outside Lymph Node | Interior of Lymph Node |
| 4 | Membrane receptor | BCR (= immunoglobulin) for antigen | TCR for antigen |
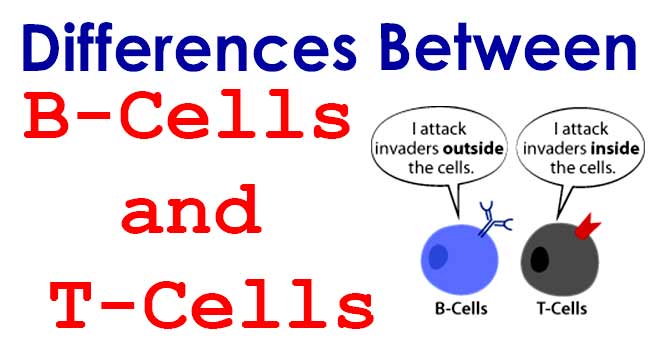
| 5 | Connections | B-cells can connect to antigens right on the surface of the invading virus or bacteria. | T-cells can only connect to virus antigens on the outside of infected cells. |
| 6 | Tissue Distribution | Germinal centres of lymph nodes, spleen, gut, respiratory tract; also subcapsular and medullary cords of lymph nodes | Parafollicular areas of cortex in nodes, periarteriolar in spleen |
| 7 | Life Span | Life span is short | Life span is long |
| 8 | Surface Antibodies | Surface Antibodies present | Absence of surface antibodies |
| 9 | Secretion | They secrete antibodies | They secrete Lymphokines |
| 10 | Function | В-cells form humoral or antibody-mediated immune system (AMI). | T-cells form cell-mediated immune system (CMI). |
| 11 | Blood | 20% of lymphocytes | 80% of lymphocytes; CD4 > CD8 |
| 12 | Formation | They form plasma cells and memory cells. | They form killer, helper and suppressor cells. |
| 13 | Movement to Infection Site | Plasma cells do not move to the site of infection. | Lymphoblasts move to the site of infection. |
| 14 | Function | Plasma cells do not react against transplants and cancer cells. | Killer cells react against transplants and cancer cells. |
| 15 | Function | Plasma cells have no inhibitory effect on immune system. | Suppressor cells inhibit immune system. |
| 16 | Function | They defend against viruses and bacteria that enter the blood and lymph. | They defend against pathogens including protists and fungi that enter the cells. |

All tha t-cells have CD3 receptor on their surface .
T helper(CD4)cells
T suppressor(CD8)cells :
T-cells block immune response by their action on t-helper cells on b-cells
Cytotoxic t(tc) cells
T-cells
Regulatory t-cells Effector t-cells
1. CD4 1.cytotoxic t-cell
2.CD8. 2.DTH
3MLR
question: how do the t-cells and b-cells react differently from infection of a virus directly versus infection via vaccine?
next
Good work.But i got a small rectification on ORIGIN,both B and T lymphocytes originate from bonemarrow[red] but they mature in different organs:bonemarrow and thymus respectively.
Thankyou
Thank you. I work in the field of bleeding disorders. As an Hemophilia and Thrombophilia Treatment Center social worker, I constantly look for educational materials for my patients and their families.
There is a mistake.. B cells are not formed in bone marrow, but in bursts (meaning pouches) eg. in appendix..
I am also intrusted in medical microbiology and virology…and I m learning many from u…many thanks
In the healthy male and female subjects, the mean concentration of Energy of cells, meaured in adenozine-triphosphat, ATP in 1 x 106 lymphocytes /ml of normal peripheral blood T lymphocytes, was 1.39 µM ATP and in B lymphocytes the concentration was 0.35 µM ATP/ml [SD = 0.41, p= 0.030].
From patients with malignant diseases, the concentration of ATP in 1 x 106 activated peripheral blood T lymphocytes/ml had a mean value of 3.06 µM ATP and the mean concentration of ATP in activated B lymphocytes/ml was 0.17 µM ATP [SD= 0.45, p = 0.05].
The mean concentration of ATP in 1 x 106 activated peripheral blood malignant CLL B lymphocytes/ml was 4.33 µM ATP but was only 0.09 µM ATP [SD= 1.5, p < 0.05] in T lymphocytes from these patients.
A strong correlation was observed between the concentration of ATP of T lymphocytes from patients withmalignant diseases and ATP concentration of B lymphocytes from samples of patients with CLL (r= 0.99) and a good correlation was observed between T lymphocytes (Th) from allergic diseases and T lymphocytes (Ts) from malignant diseases (r = 0.94).
The difference of energy between anaerobic ATP in B lymphocytes from CLL and aerobic ATP in T lymphocytes from healthy subjects havebeen calculated in value of 2.68 µM ATP, suggests the process of carcinogenesis, in malignant diseases.
Dr. Aurel
hierarchy:B-cells are soldiers where T-cells include generals, commanders, officers and even military police.