| S.N. | Characteristics | Chickenpox | Smallpox |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Causative Agent | Varicella Zoster Virus (Herpes Virus) | Variola virus (Pox Virus) |
| 2 | Incubation period | 14-21 days | 7-17 days |
| 3 | Severity | Chickenpox is less deadly comparing to small pox. | Smallpox is deadly severe comparing to chicken pox. |
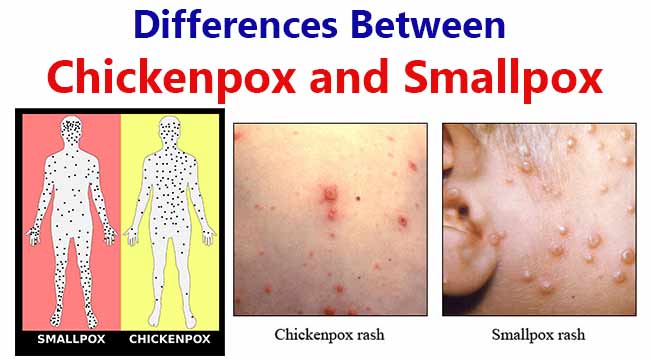
| 4 | Lesions | Lesions first appear on the face or trunk. | Lesions first appear in the throat or mouth, then on the face, or on the upper arms. |
| 5 | Rash Lesions | Lesions develop in successive fashion. While some are new, others are crusting over (in “crops”). | Lesions develop at the same time, and they look alike on any one section of the body, such as the abdomen, arms, or face. |
| 6 | Initial Symptoms | 0 to 2 days of mild illness pass before the rash develops. | 2 to 3 days of severe illness pass before the rash develops. |
| 7 | Rash Lesions | Lesions change rapidly, crusting over within 24 hours. | Lesions change slowly, scabbing over after 9 to 15 days. |
| 8 | Rash Lesions | Lesions sit on the skin surface and look like small blisters. | Lesions become firm, dome-shaped, and deep in the skin. |
| 9 | Rash Lesions | Rash rarely develops on palms and soles. | Rash commonly develops on palms of the hands and soles of the feet. |
| 10 | Rash Lesions | Lesions are most concentrated on the torso, with fewest on the hands and feet. Lesions can affect the face and scalp, but rarely affect the entire body equally. | Lesions are most concentrated on the face, hands, and feet. |
| 11 | Rash Lesions | No illness precedes the chickenpox rash. | Malaise, fever, rigors, vomiting, headache and backache precede the rash by two to three days. |
| 12 | Scabs | Scabs that are not infectious begin to form four to seven days after the rash appears. | Scabs that can be infectious begin to form 10 to 14 days after the rash appears. |
| 13 | Scabs | Scabs fall off within 14 days after the rash begins. | Scabs fall off 14 to 28 days after the rash begins. |
| 14 | Pocks | Pocks are more superficial. | Pocks are buried deep in the dermis. |
| 15 | Vesicles | Vesicles collapse on puncture. | Vesicles do not collapse on puncture. |
| 16 | Evolution of Pocks | Asynchronous | Synchronous |
| 17 | Prevalence | Chickenpox is still prevailing. | Smallpox has been eradicated from the earth. |
| 18 | Fever | Fever occurs with each crop of vesicles | Fever subsides with development of rash,
may appear again with formation of pustules (secondary rise of temperature) |
Similar Posts:
- Zika Virus- Structure, Genome, Symptoms, Transmission, Pathogenesis, Diagnosis
- Histoplasma Capsulatum – Habitat, Morphology, Epidemiology, Virulence Factors, Treatment + More
- Techniques of Virus Cultivation
- Cryptococcus Neoformans – Habitat, Morphology, Epidemiology, Virulence Factors, Treatment + More

n distinguishing small pox and chicken pox lacks in the aspect of which system is affected by each of them and the severity plus damage caused and types of foods and beverages required in each.
I had cowpox as a child (in the 70s) I want to know if I can still catch chicken pox or do I have immunity?