Antibody (Ab) also know as Immunoglobulin (Ig) is the large Y shaped protein produced by the body’s immune system when it detects harmful substances, called antigens like bacteria and viruses. The production of antibodies is a major function of the immune system and is carried out by a type of white blood cell called a B cell (B lymphocyte), differentiated B cells called plasma cells. The produced antibodies bind to specific antigens express in external factors and cancer cells.
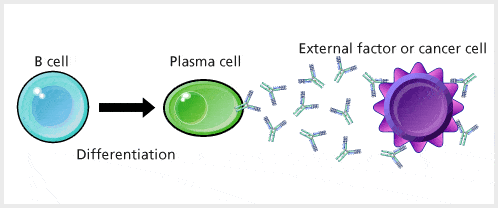
Structure of Antibody
Antibodies are heavy (~150 kDa) globular plasma proteins. The basic structure of all antibodies are same.
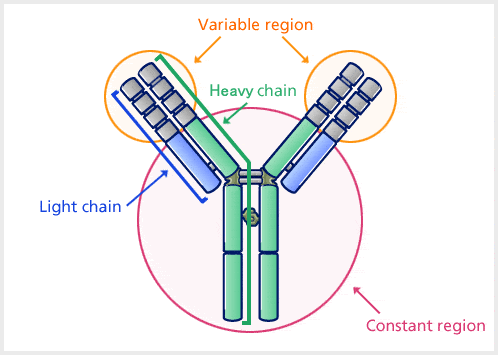
Source: Kyowa Hakko Kirin Co., Ltd
There are four polypeptide chains: two identical heavy chains and two identical light chains connected by disulfide bonds. Light Chain (L) consists polypeptides of about 22,000 Da and Heavy Chain (H) consists larger polypeptides of around 50,000 Da or more. There are five types of Ig heavy chain (in mammal) denoted by the Greek letters: α, δ, ε, γ, and μ. There are two types of Ig light chain (in mammal), which are called lambda (λ) and kappa (κ).
An antibody is made up of a variable region and a constant region, and the region that changes to various structures depending on differences in antigens is called the variable region, and the region that has a constant structure is called the constant region.
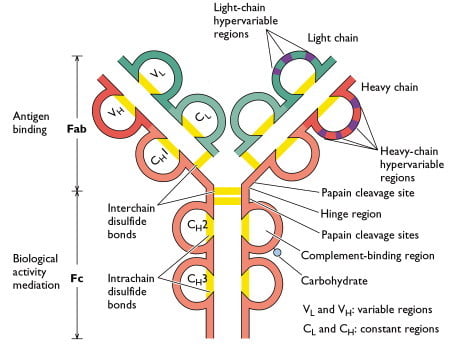
Source: Sino Biological Inc.
Each heavy and light chain in an immunoglobulin molecule contains an amino-terminal variable (V) region that consists of 100 to 110 amino acids and differ from one antibody to another. The remainder of each chain in the molecule – the constant (C) region exhibits limited variation that defines the two light chain subtypes and the five heavy chains subclasses. Some heavy chains (α, δ, γ) also contain a proline-rich hinge region. The amino terminal portions, corresponding to the V regions, bind to antigen; effector functions are mediated by the carboxy-terminal domains. The ε and μ heavy chains, which lack a hinge region, contain an additional domain in the middle of the molecule. CHO denotes a carbohydrate group linked to the heavy chain.
Classes/Types of Antibody
Serum containing antigen-specific antibodies is called antiserum. The 5 types – IgG, IgM, IgA, IgD, IgE – (isotypes) are classified according to the type of heavy chain constant region, and are distributed and function differently in the body.
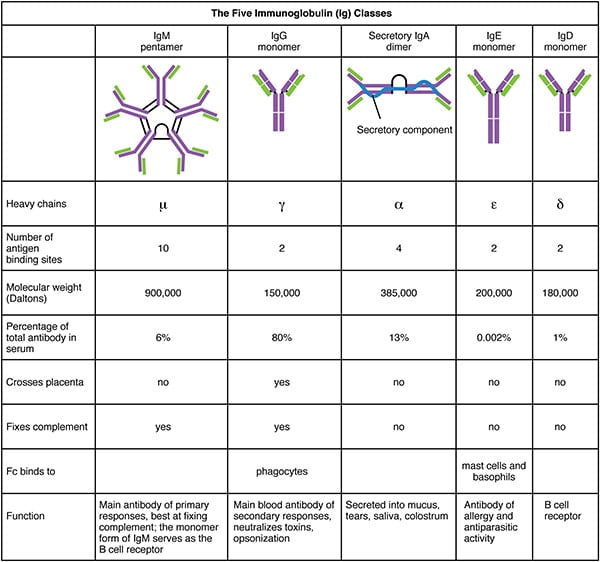
Functions of Antibody
- IgG provides long term protection because it persists for months and years after the prescence of the antigen that has triggered their production.
- IgG protect against bacteris, viruses, neutralise bacterial toxins, trigger compliment protein systems and bind antigens to enhance the effectiveness of phagocytosis.
- Main function of IgA is to bind antigens on microbes before they invade tissues. It aggregates the antigens and keeps them in the secretions so when the secretion is expelled, so is the antigen.
- IgA are also first defense for mucosal surfaces such as the intestines, nose, and lungs.
- IgM is involved in the ABO blood group antigens on the surface of RBCs.
- IgM enhance ingestions of cells by phagocytosis.
- IgE bind to mast cells and basophils wich participate in the immune response.
- Some scientists think that IgE’s purpose is to stop parasites.
- IgD is present on the surface of B cells and plays a role in the induction of antibody production.

Great article for an overview of antibodies! Thanks for writing this.
If IgG is low in its strength ” so to speak” does that mean the virus and or bacterial infection has surpassed it in the fight to protect the individual….
Does all the antibody classes have the same number of constant regions. If no, please explain to me why with vivid structure of the different antibody classes. It’s an assignment that I need to submit. Please
What does ig stand for…in full
immunoglobulin
immunoglobin which means antibody
Ig means immunoglobulin
Globulin is a protein
why does the heavy chain segment show 4 cdr regions when there is only 3?
why there’s no IgB, IgC, IgF, IgH, IgI, IgJ, IgK, IgL
There are 5 types of heavy chain constant region; Mu, Gamma, Alpha, Epsilon, Delta. We take the first letter of each Greek letter to denote IgA, IgG, IgE, IgD and IgM respectively.
please write names of anti bodies
antibody G
antibody A
antibody M
antibody E
antibody D
antibody = immunoglobin