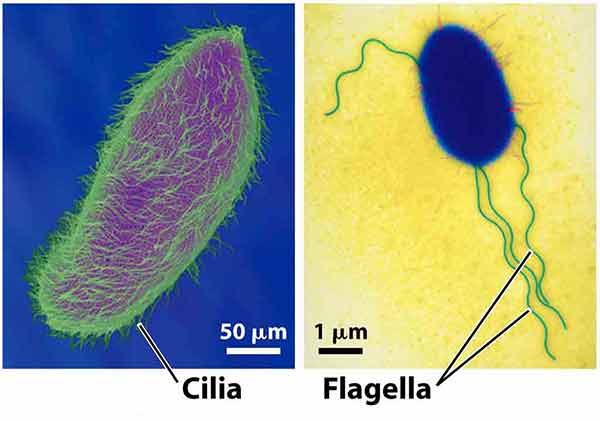
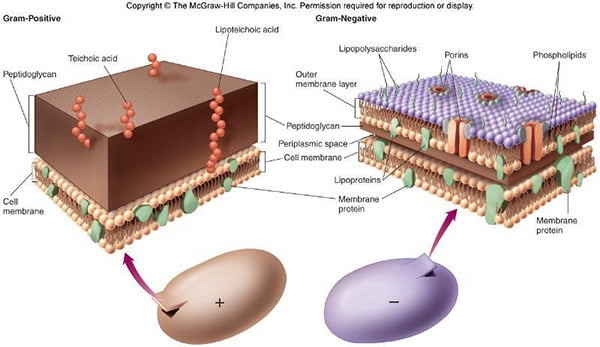
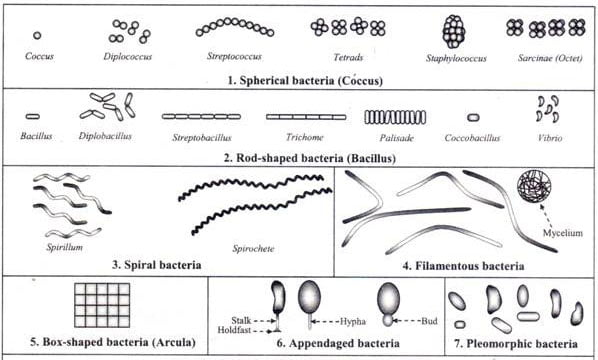
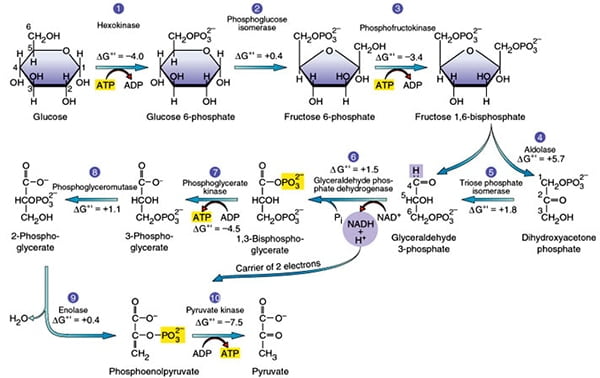
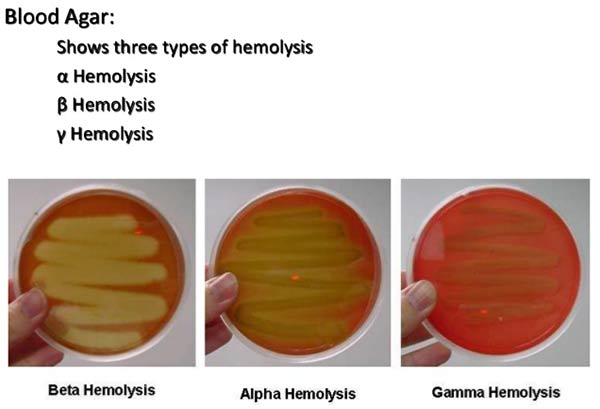
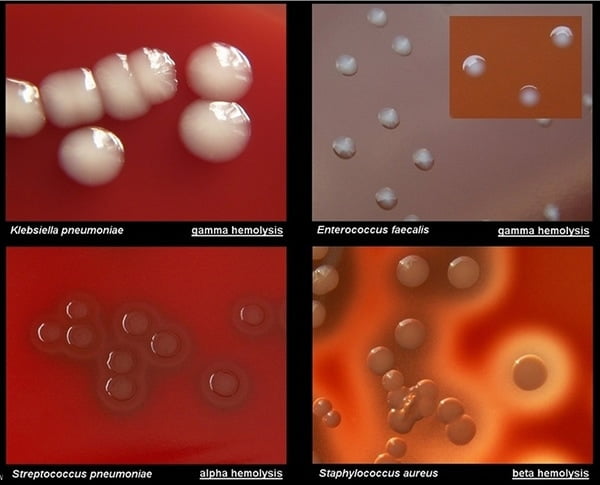
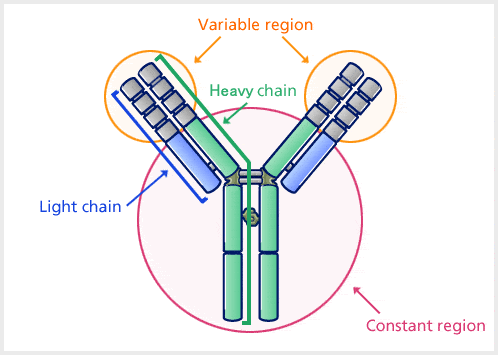
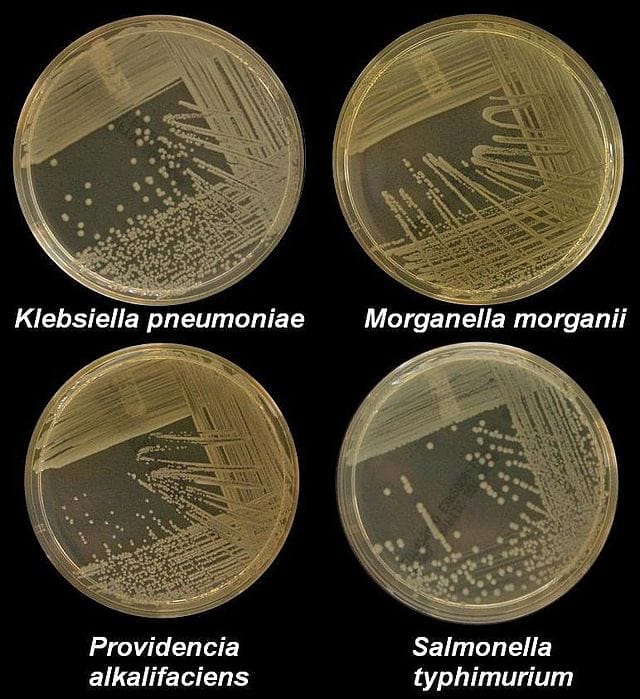
Differences Between Cilia and Flagella
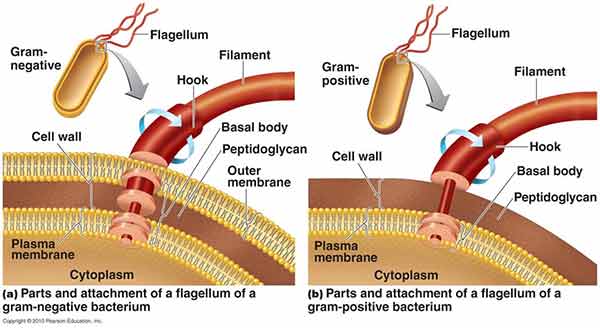
Flagella are the complex filamentous cytoplasmic structure protruding through cell wall. These are unbranched, long, thread like structures, mostly composed of the protein flagellin, intricately embedded in the cell envelope. Cilia are slender, microscopic, hair-like structures or organelles that extend from the surface of nearly … Read more