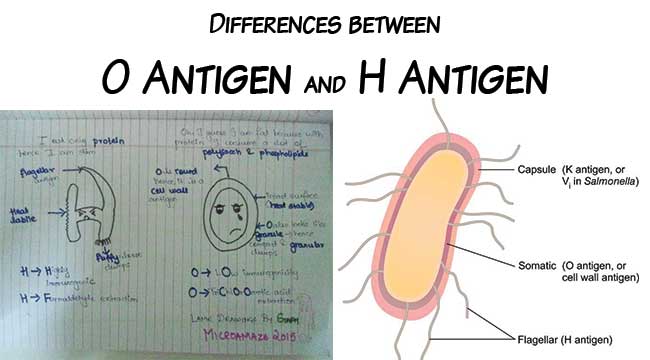
Difference between O Antigen and H Antigen
The antigen used to define serological test of Salmonella include Somatic O antigen, Flagellar H antigen and Vi antigen (Capsular antigen). Some of the differences between O Antigen and H Antigen are as follows: S.N. Characteristics O Antigen H Antigen 1. Types Somatic Antigen Flagellar … Read more