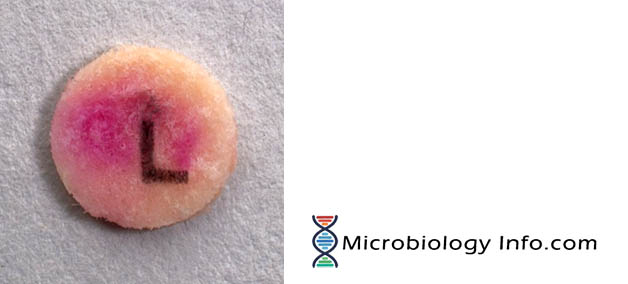
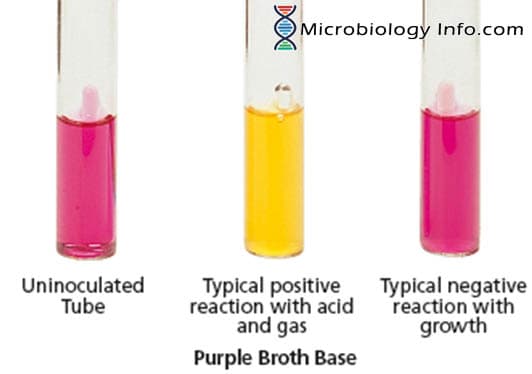
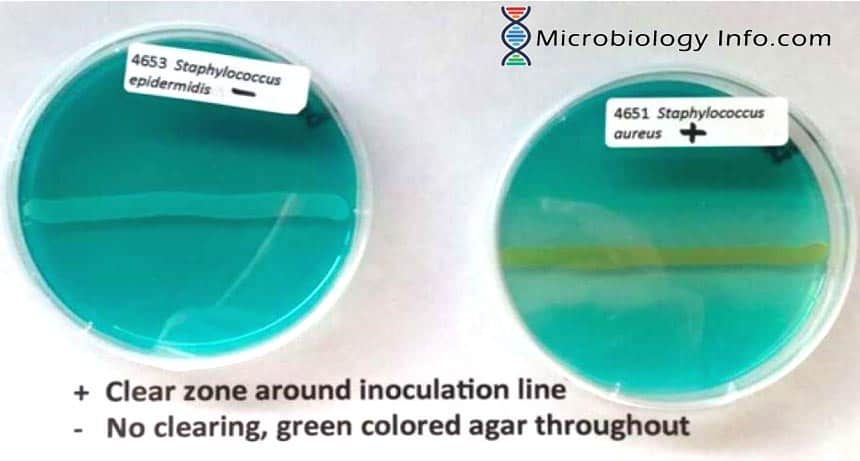
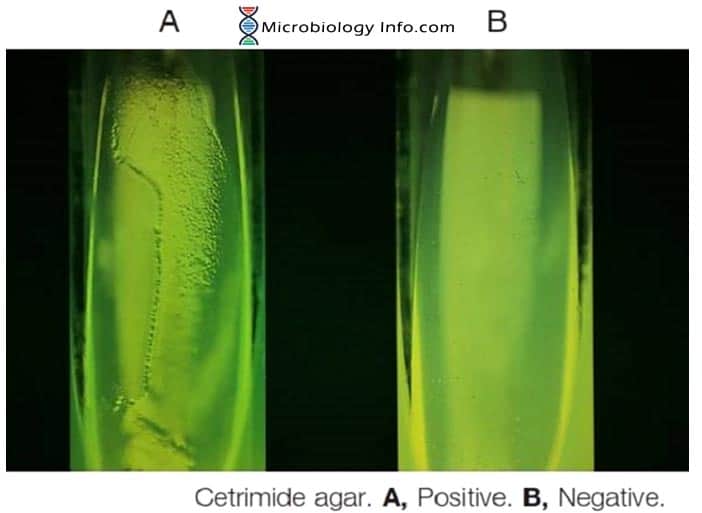
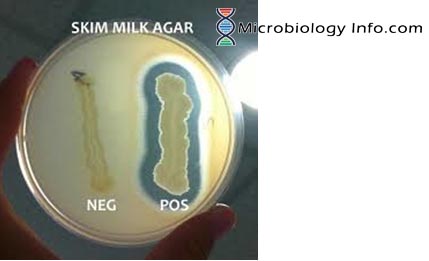
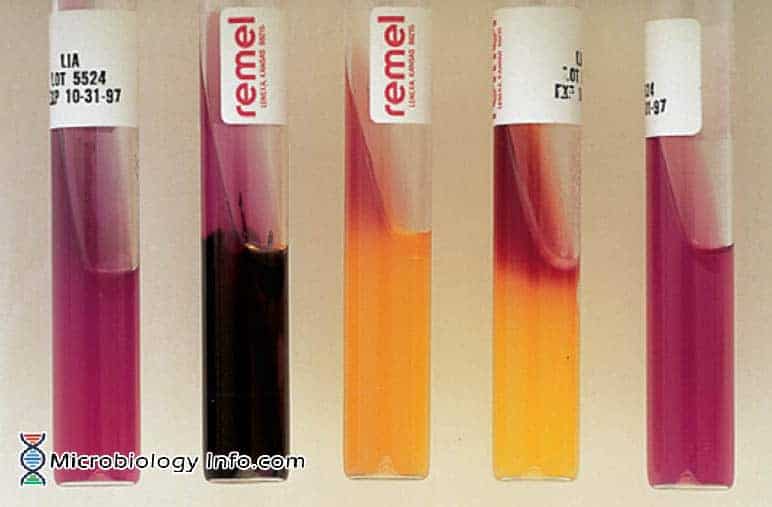
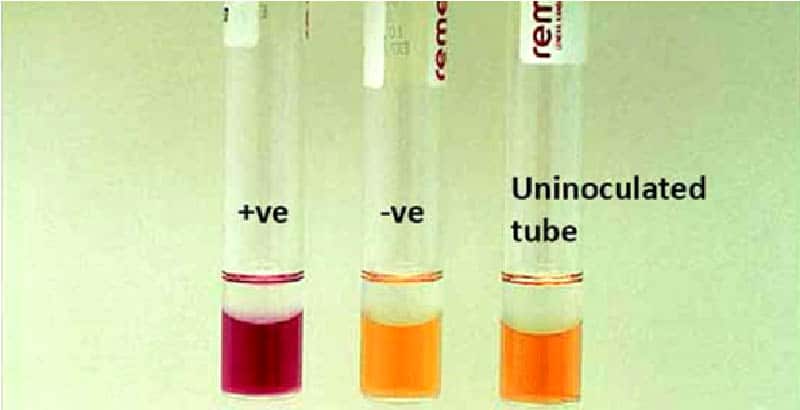
Leucine amino peptidase (LAP) Test – Procedure, Uses and Interpretation
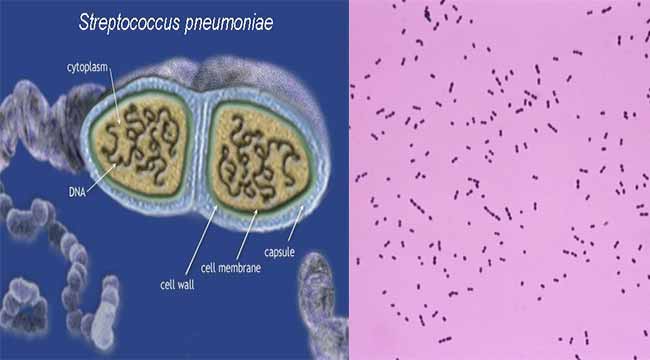
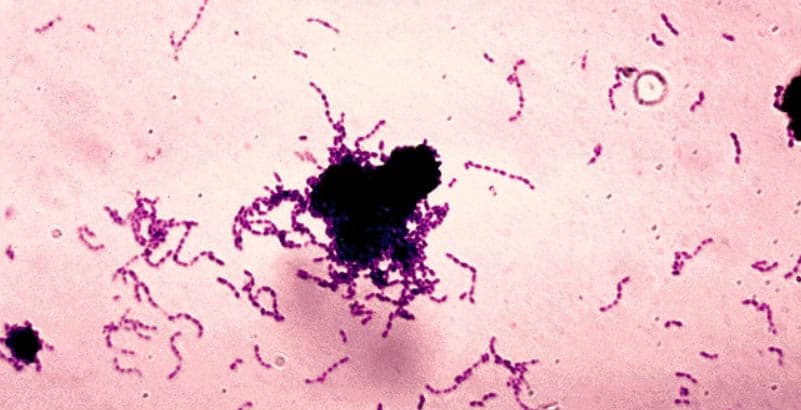
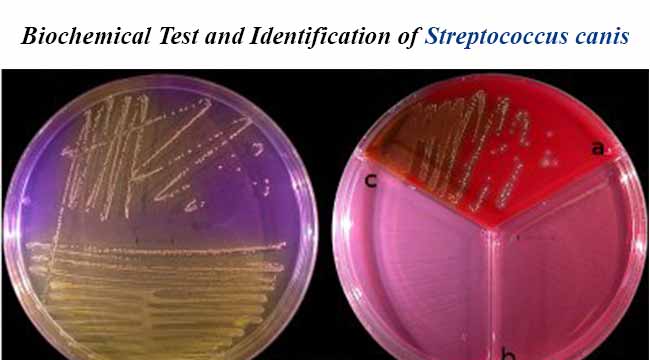
Leucine amino peptidase (LAP) test is a rapid test for detection of enzyme leucine aminopeptidase. Leucine- β- napthalamide impregnated disk serves as a substrate for the detection of leucine aminopeptidase. This test is usually used, in conjunction with other tests, for the identification of streptococci and … Read more