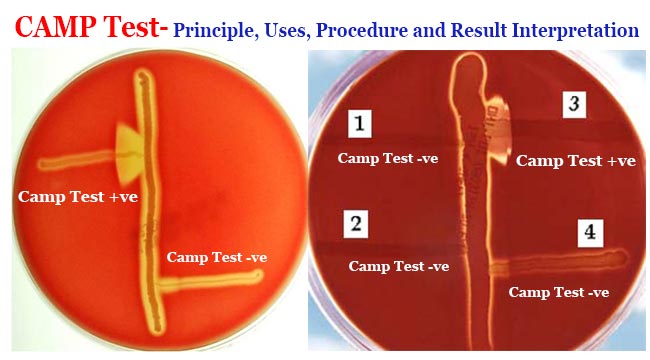
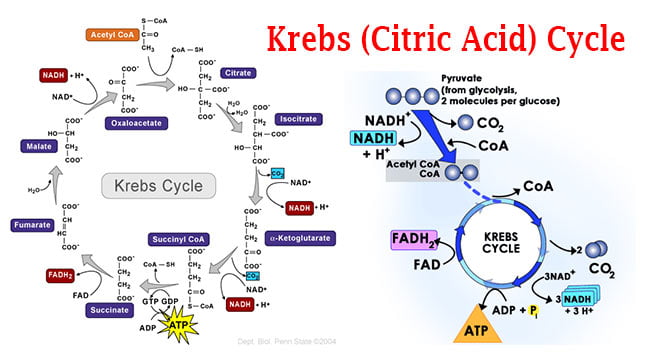
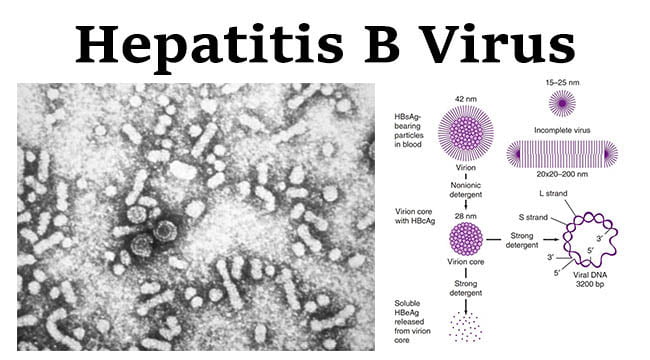
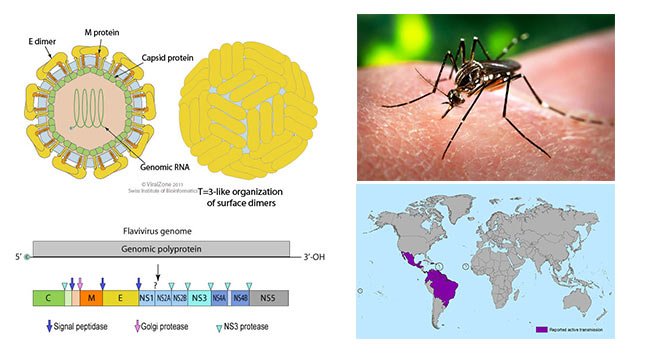
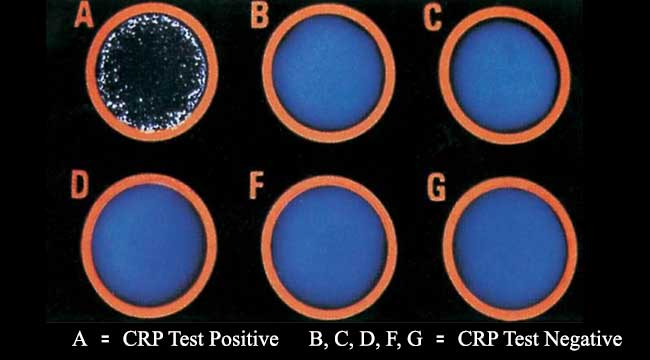
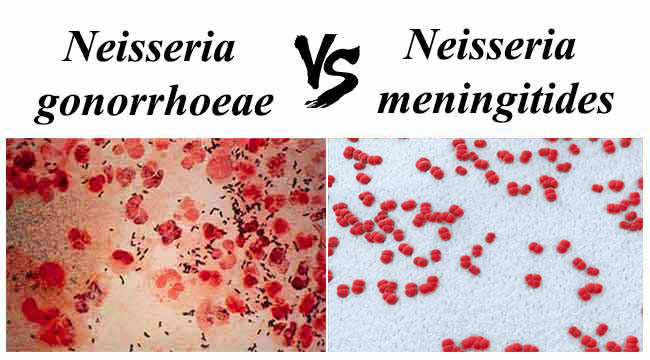
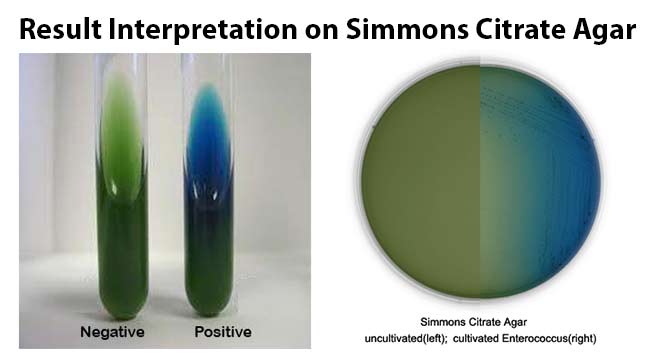
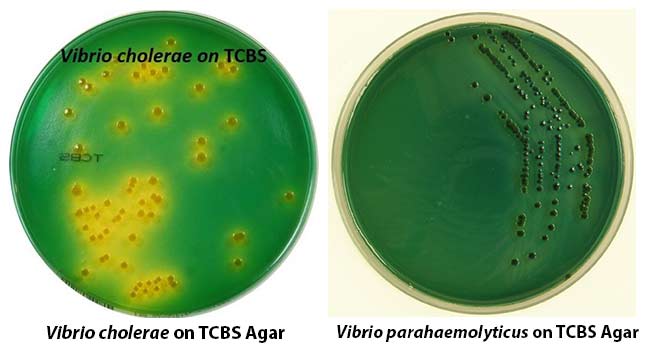
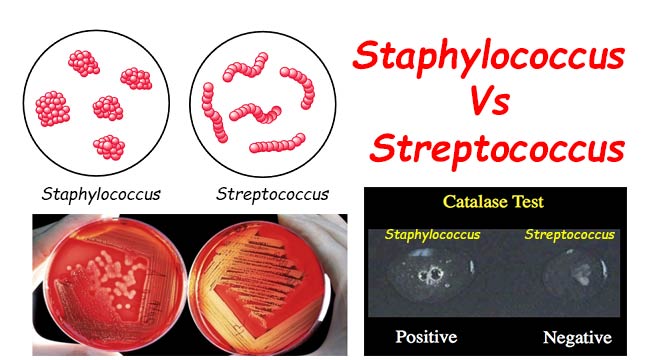
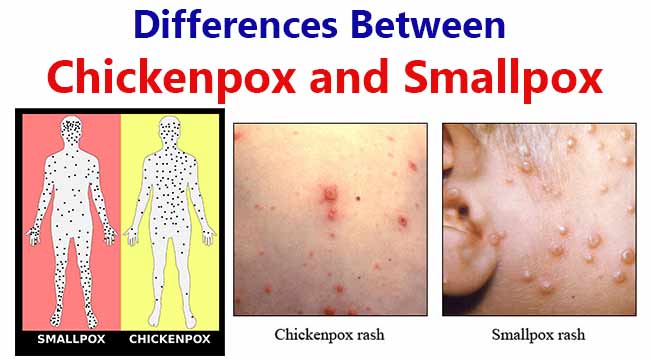
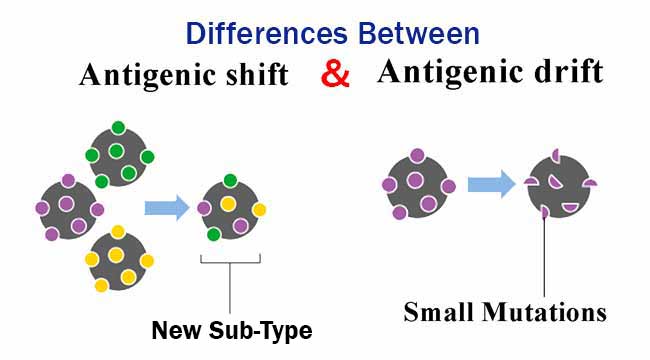
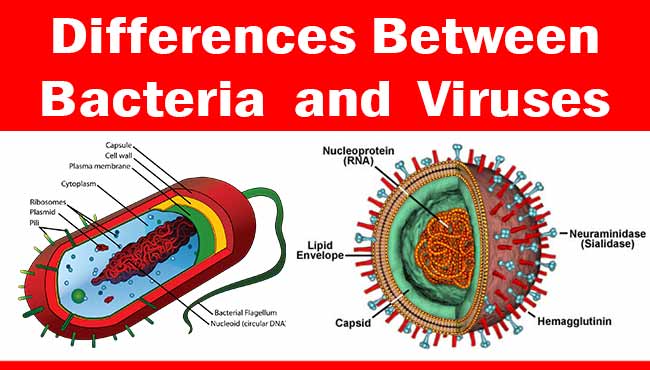
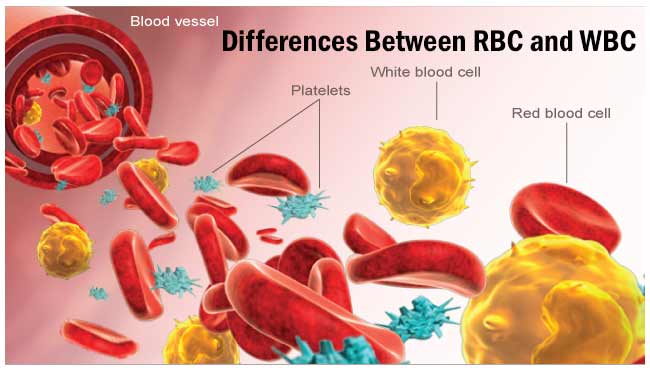
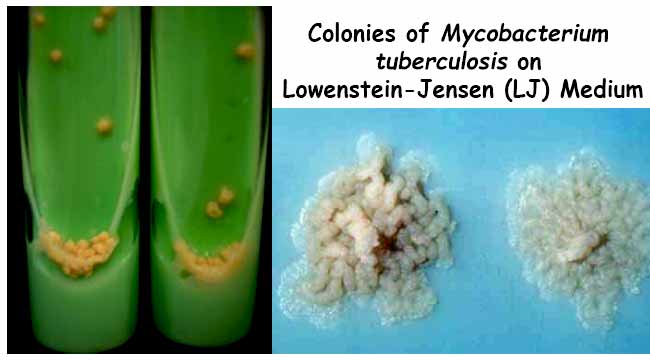
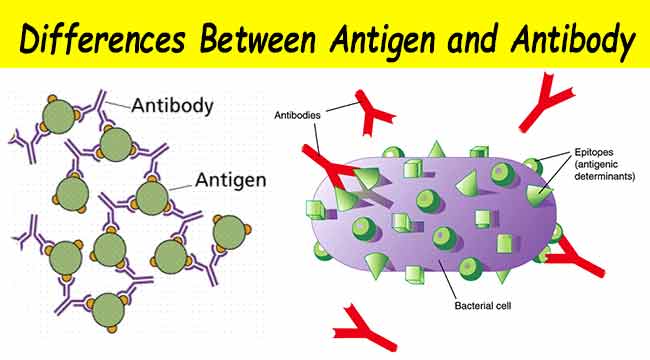
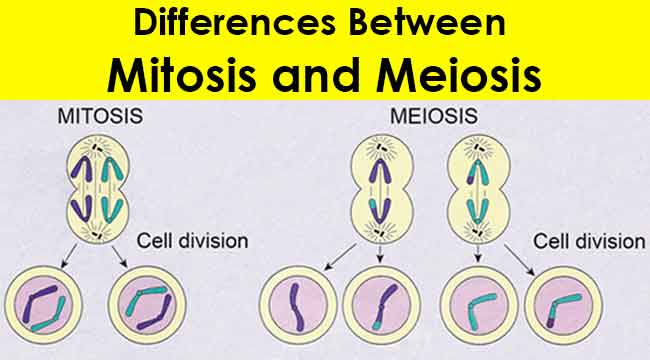
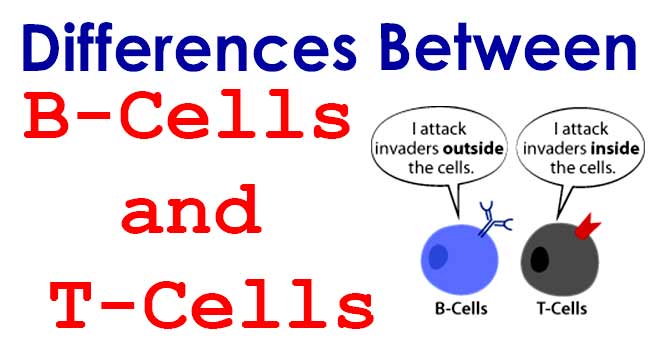
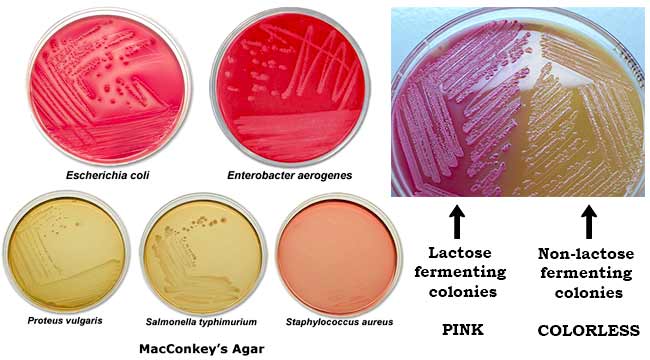
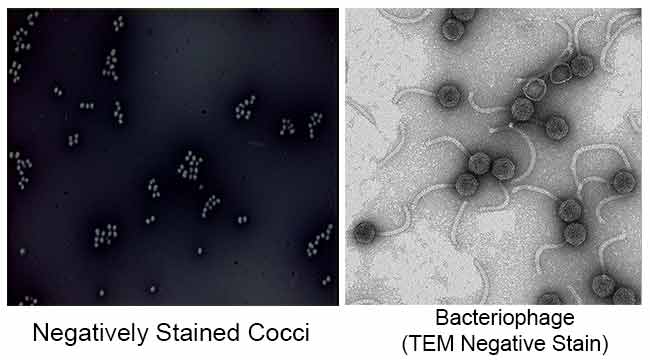
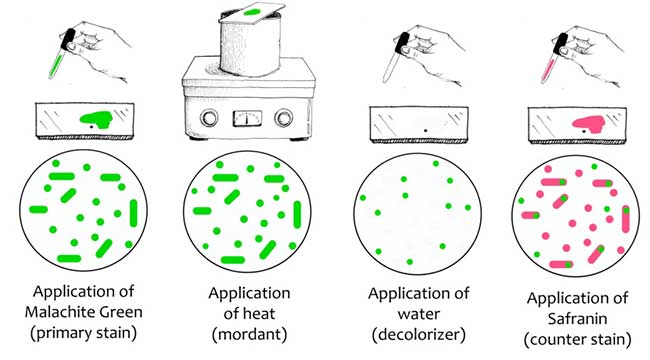
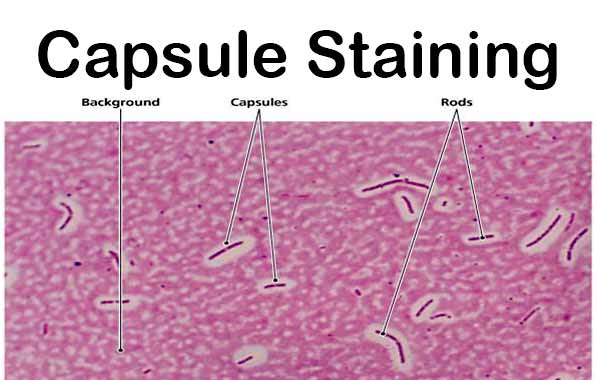
CAMP Test- Principle, Uses, Procedure and Result Interpretation
CAMP test is used to distinguish the species Streptococcus agalactiae from other species of beta-hemolytic Streptococcus. S. agalactiae, a member of the Lancefield Group B streptococci, is one of the causative agents of mastitis in cows. CAMP is an acronym for the authors of this … Read more