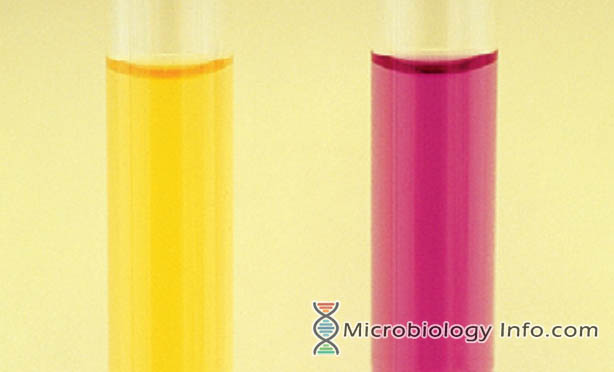
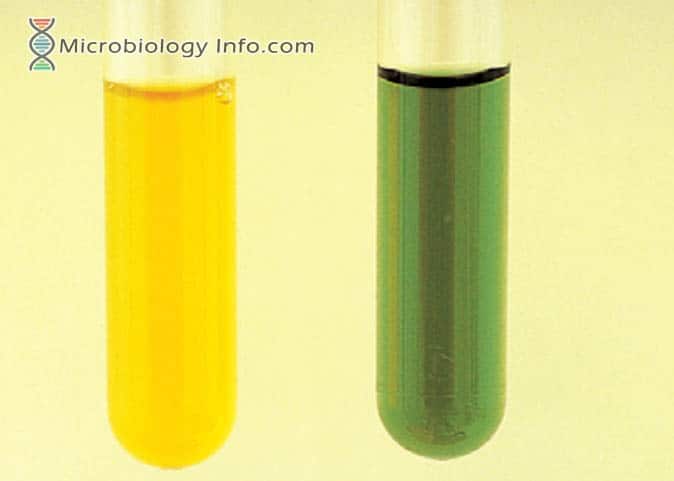
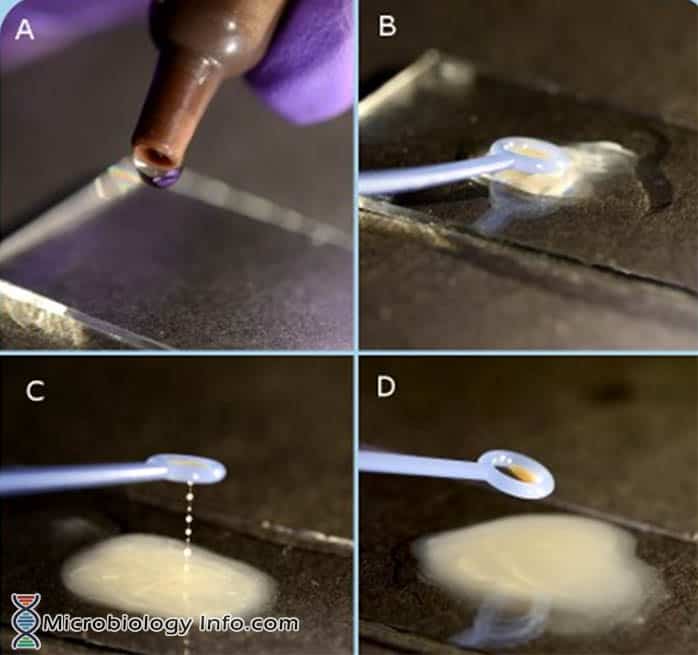
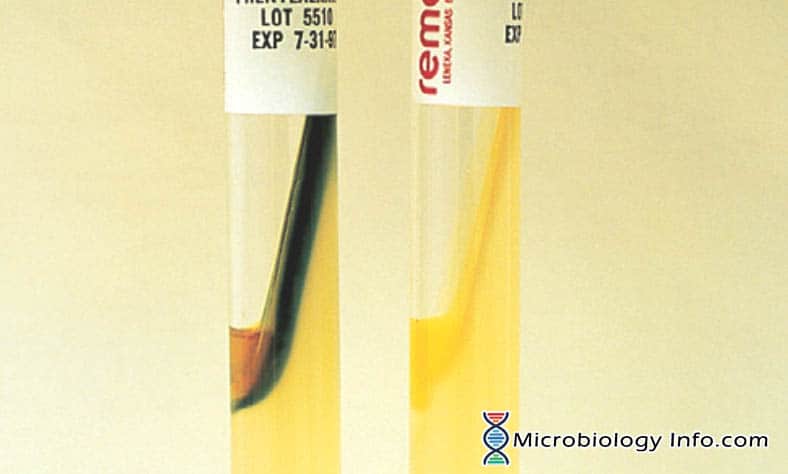
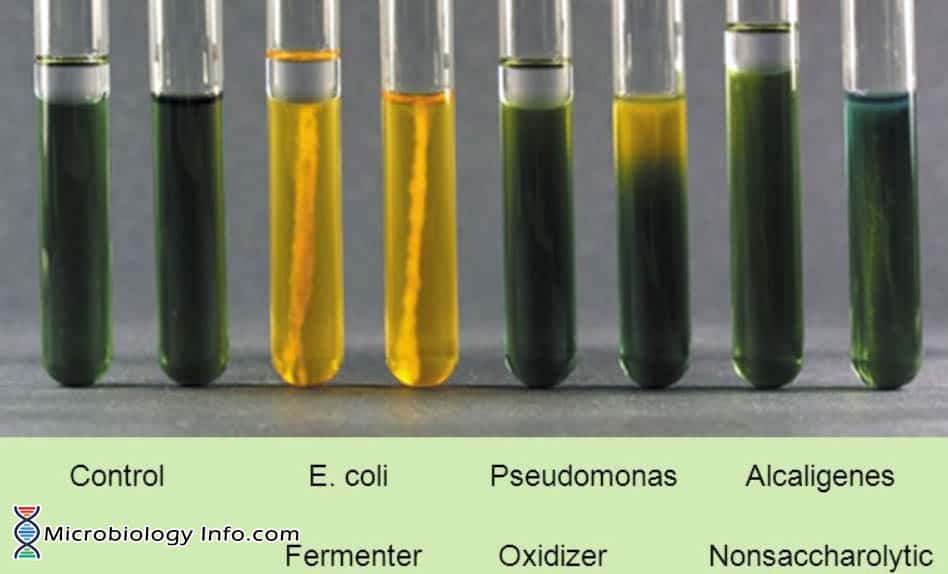
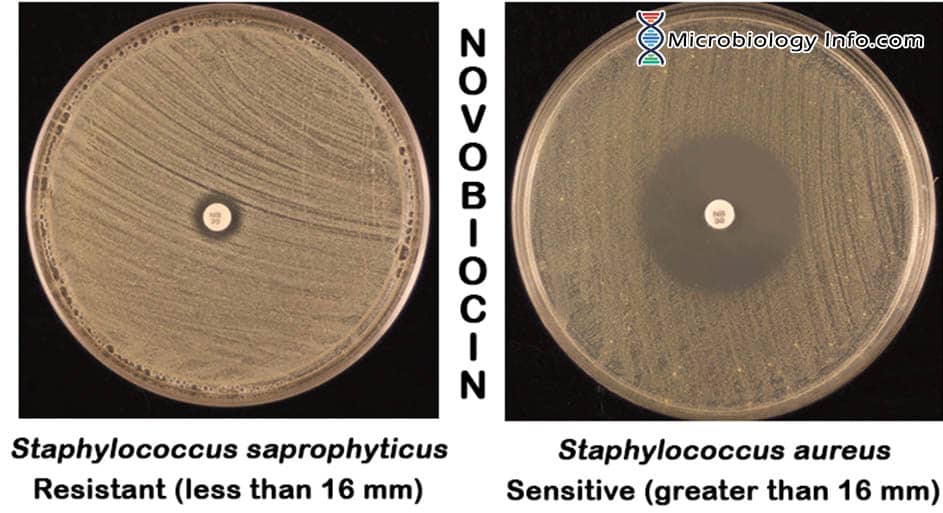
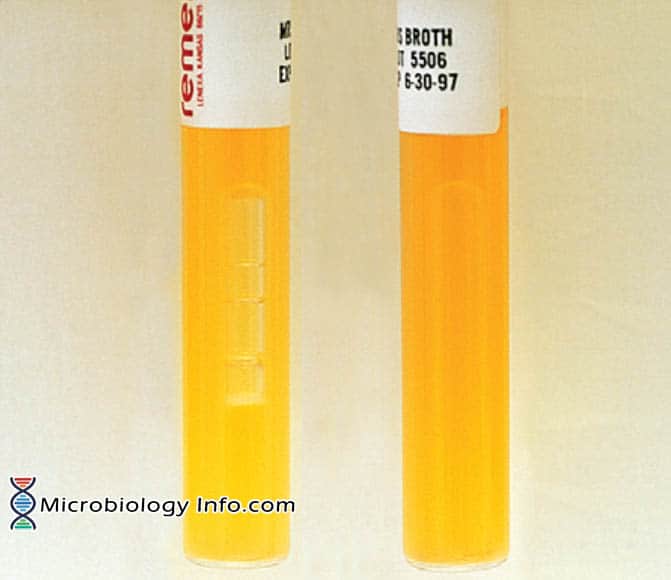
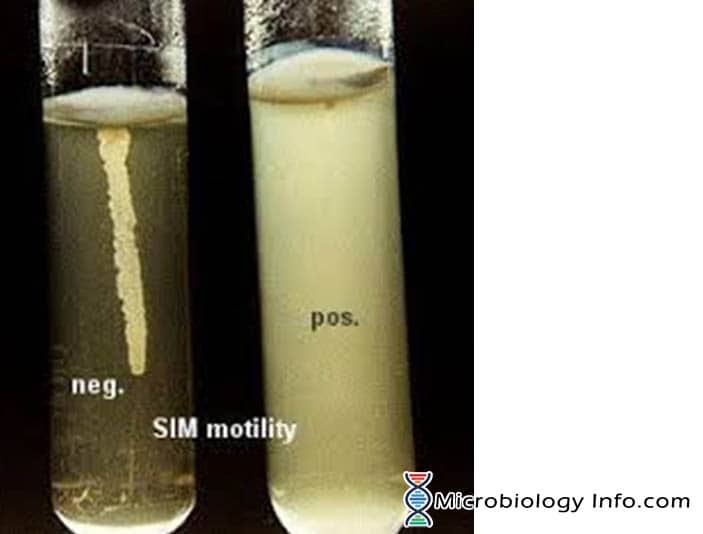
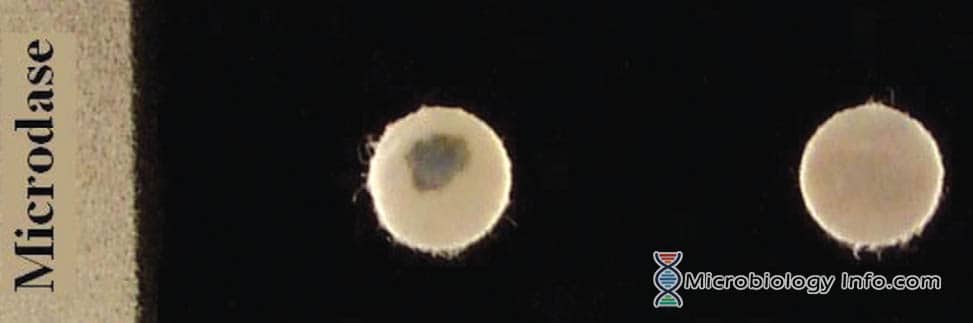
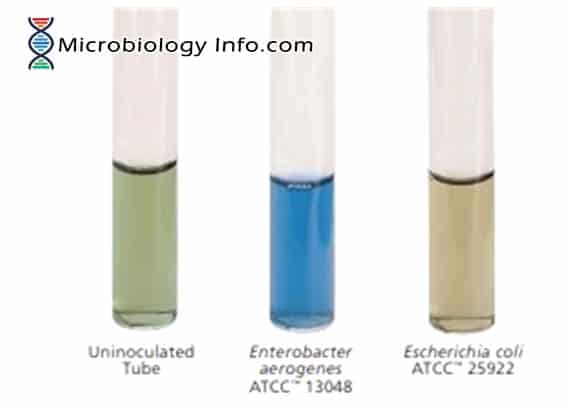
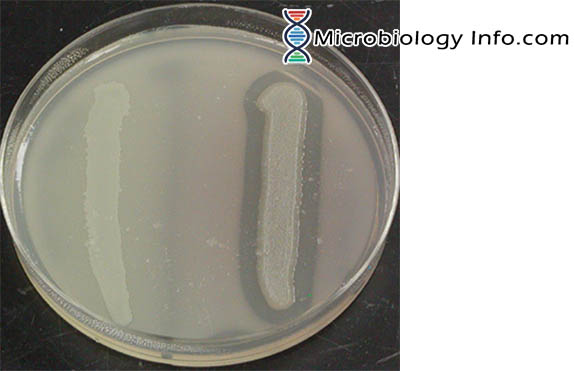
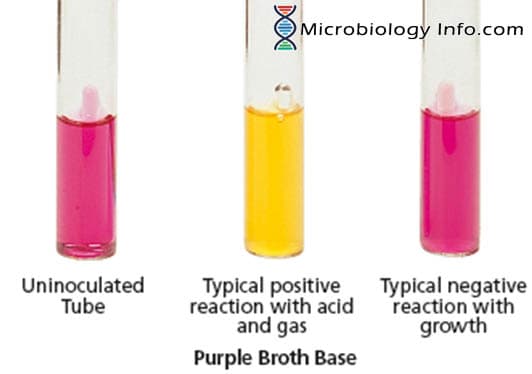
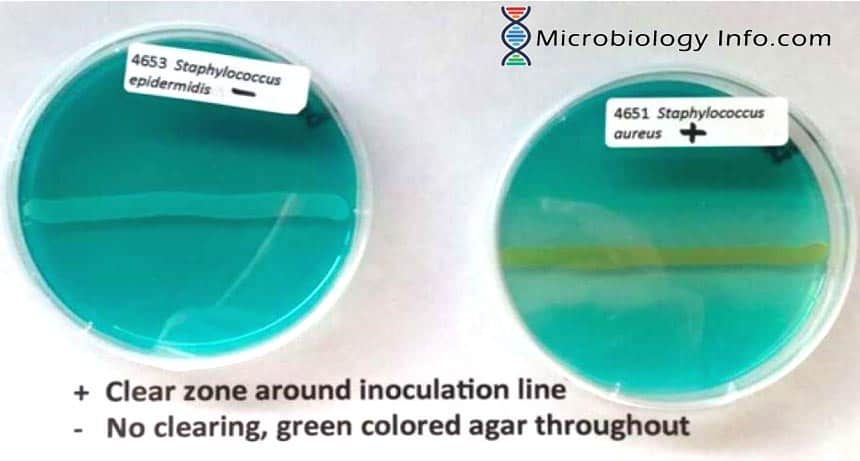
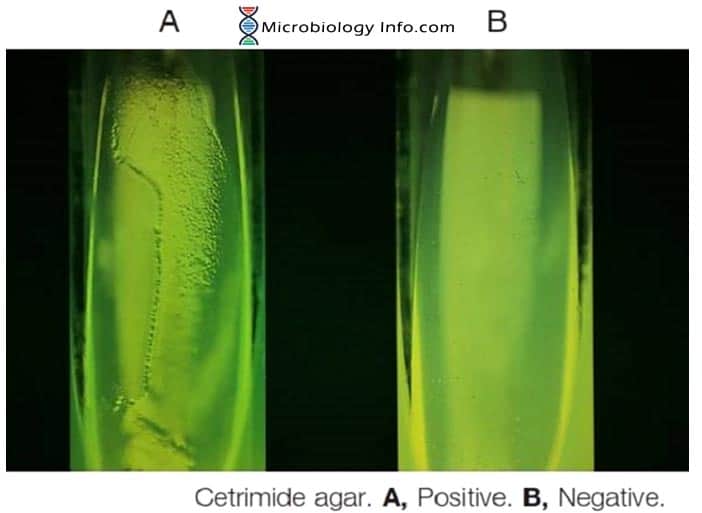
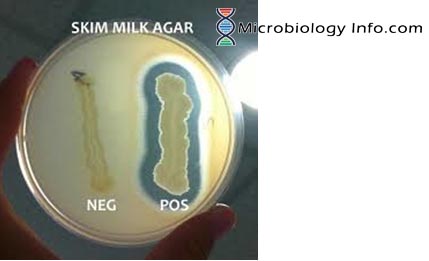
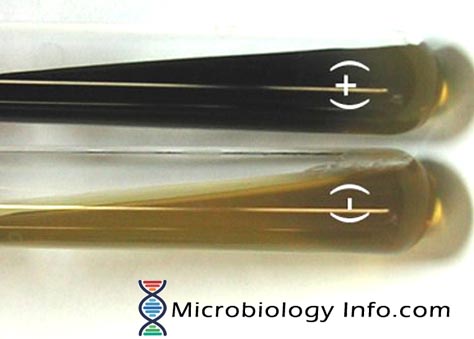
X and V factor Test – Principle, Procedure, Uses and Interpretation
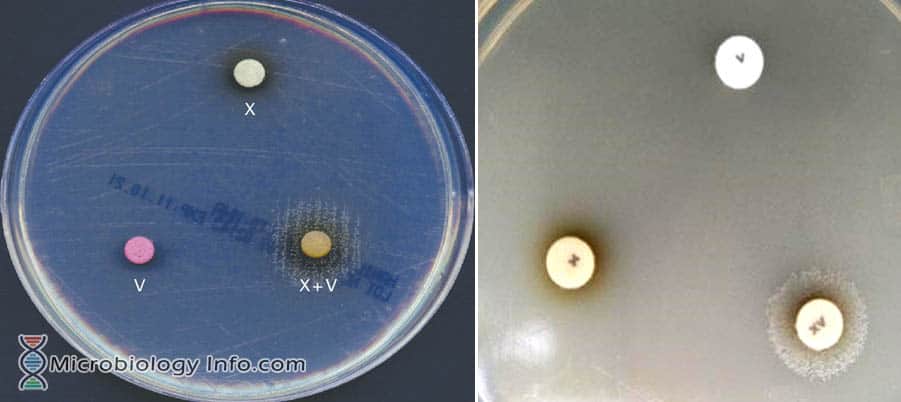
Haemophilus spp are small, pleomorphic, gram-negative bacilli or coccobacilli with random arrangements. A clinically important species of the genus, influenzaeis a fastidious organism which grows best at 35-37°C with ~5% CO2 and in the presence of special accessory growth factors called X and V factors. X factor … Read more